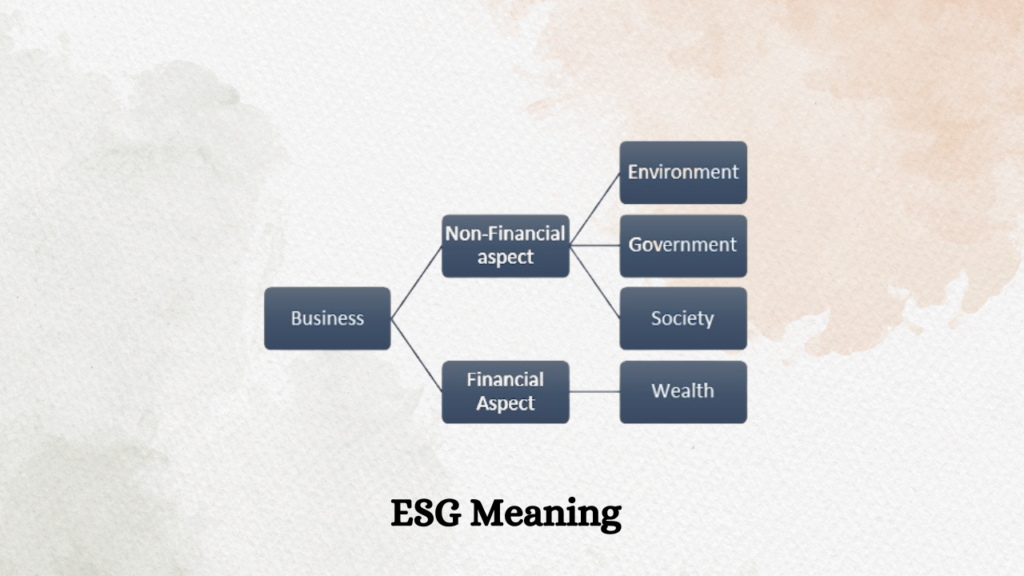
In the last few decades business has evolved a lot, its motive is not just confined to making profit. Scope of business has increased. Companies are to be evaluated beyond traditional financial metrics. Financial performance of a company fails to evaluate the qualitative success.
A business entity needs to keep on improving on their non-financial aspects as well. ESG focuses on such aspects of the business that evaluate qualitative success for a business unit.
ESG Meaning in Business
ESG stands for Environment, Social, and Governance, these are the criteria used by internal and external stakeholders of the companies to evaluate the responsibility, sustainability and risk profile.
Concept of ESG has evolved over time because of various movements that focused on health care, safety concerns, eco-friendly options and corporate philanthropy. ESG also affects how the capital would be allocated.
ESG Factors Discussed: All details here
Now we will be discussing 3 factors of ESG in detail:
1. Environment
Business operations impact the natural environment. For a sustainable development and healthy wealth maximization of business it is important that the following factors are taken into consideration:
Carbon Emissions: A company emits greenhouse gases directly or indirectly through its operations or even products. The amount of greenhouse being produced must be in check.
Resource Utilization: For running business various resources are consumed, water, energy raw materials in different forms. Companies have to be evaluated in the efforts to use the resources to the optimum level.

Wastage Disposal: It is very important how a company manages its wastage cycle, how much the company is devoted to reduce the wastage and recycle it when possible. The companies must have the policies for Reduce, Reuse and Recycle.
Guarding Biodiversity: Company’s activities disturb the immediate environment the most, that is the biodiversity. The possible harm towards wildlife, natural habitats, deforestation and all the possible impacts must be assessed.
Environment Stewardship: This means the company’s policy in relation with environmental impact assessment and compliance with environmental regulations.
Companies must adopt sustainable practices and minimize their environmental harm for long-run success.
2. Government
A company is a large organization with great influential power thus it is important for regulatory bodies to direct and control the activities of the unit to meet the ethical and legal standards.
Corporate Ethics: The ethics and culture followed depends upon the integrity of a company’s leadership, this is achieved by possessing a sense of accountability and ethical conduct.
Transparency: To what extent a company provides the information accurately and transparently to its stakeholders, that includes financial reports, and ESG performance disclosure.
Shareholders Engagement: Company must protect and respect the rights of its shareholders, and allow them to participate in the matters more closely, with better voting rights and engagement initiatives.

Risk Management: An inherent part of business is risk, risk management is a company’s ability to identify, assess and mitigate risk as much as possible.
Compliance and Legal Standards: Company’s activities and policies must be in parallel with laws and regulations, e.g., labour law, environment regulations. As a part of ESG plan a company must practice transparency, accountability and ethical leadership, this helps in building trust of various stakeholders.
3. Society
Social factors in ESG means how the company is interacting with and has an impact on the people, including its employees, customers and other such stakeholders. Some key considerations would be:
Human Rights: This is related to issues such as fair labour, workplace diversity and sense of inclusion, employee safety measures, health facilities.
Community service: This means how a company engages with communities, like with philanthropic activities, community development initiatives and efforts for tackling social challenges.
Customer Satisfaction: It is integral that the company meets needs and expectations of its customers, through the product quality and services rendered.

Safety Standards: Any product or service must be safe to be offered to the customers after going through all necessary checks.
Social Impact: What is the social impact of the company’s existence over the society. The factors could be affordability, access to essentials, contribution to social development and progress.
Stakeholders engagement: This is about management of a company’s relationship with its diverse stakeholders, like the investors, employees, suppliers, regulators etc.
Companies with healthy social performance are those which prioritize the well-being of their employees and communities, and maintain positive relationships with the stakeholders, actively contributing to the welfare of the society.
Benefits from ESG PLANNING
In today’s era business needs to show how they are not just making profit but as well doing good for the environment, society, and what is their vision for their various stakeholders.
Those who achieve this enjoy an advantage over other competitors who ignore it. There is a great benefit in doing this as well, like getting better employees and their retention, saving money in the long run, attracting investors, etc.
ESG is part of a long-term plan, and every company has its own strategy to achieve this. Doing well in this area helps a company build its reputation and make things run smoothly.
Also Read:

